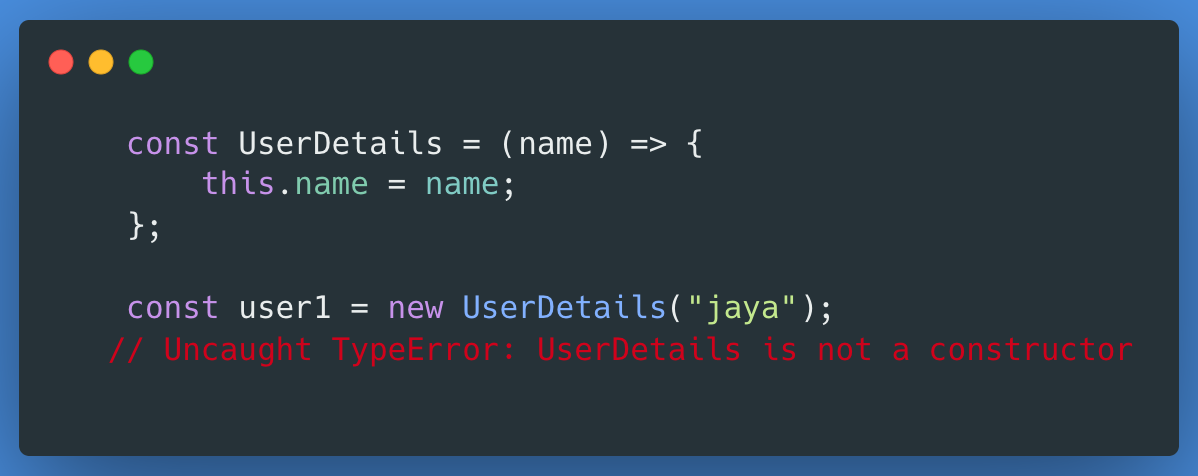
The arrow function cannot be invoked with the new keyword, because arrow functions don’t have a constructor. If you try to instantiate with a new keyword it will throw an error.
No own this (call, apply & bind won’t work as expected)
In a traditional function, its internal this value is dynamic, it depends on how the function is invoked. For example:

Unlike regular functions, arrow functions don’t have their own this binding. If we access this in the arrow function it will return the this of the closest non-arrow parent function.

The value of this in the arrow function is determined at the time of declaration and never changes. So call, apply, bind cannot change the value of the arrow function this.
Comments
Post a Comment